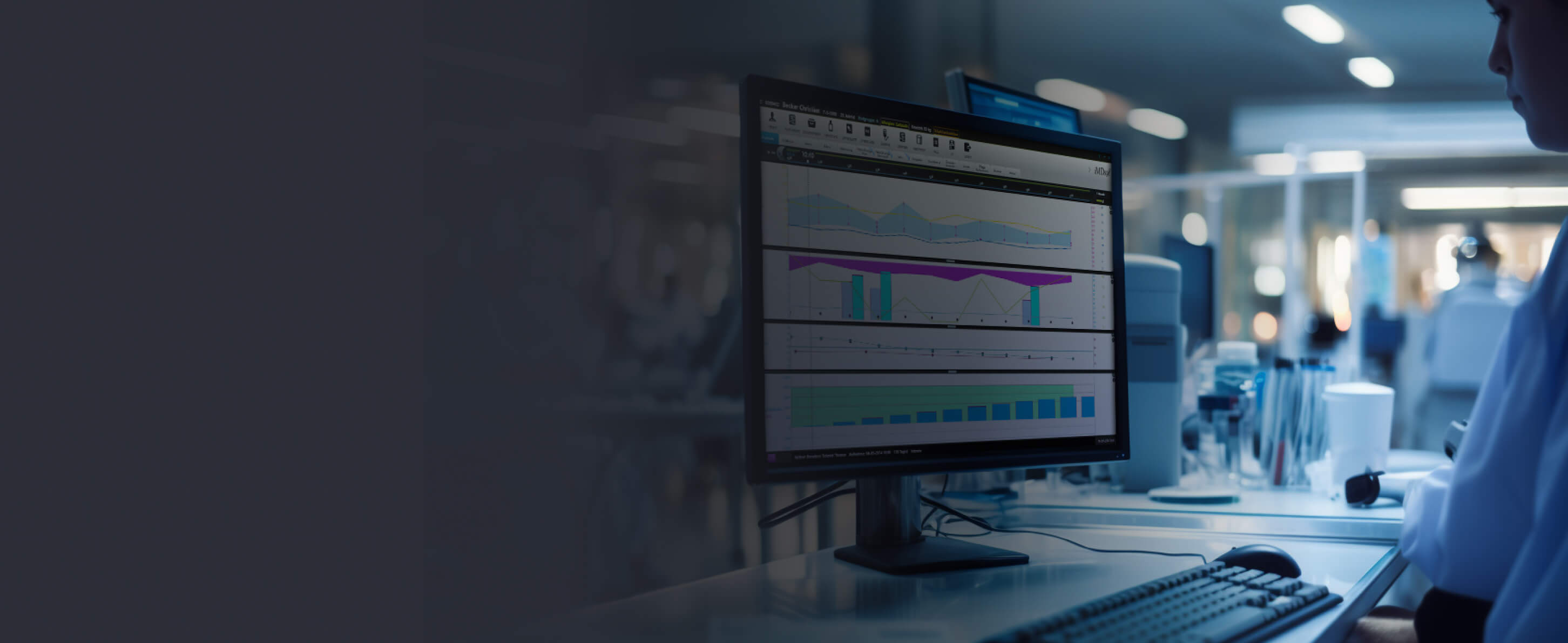
Continuous measurement of mechanical power is necessary to establish a safe protective strategy during mechanical ventilation with the aim to minimize ventilation induced lung injury (VILI), an acute lung injury affecting the airways and parenchyma which is mostly seen in patients ventilated for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). In this article, the authors developed a simplified equation to calculate dynamic mechanical power (MPdyn) at the bedside, using IMDsoft-MetaVision to record mechanical ventilator breathing parameters every minute from a total of forty adult patients hospitalized with ARDS. This equation was compared to the standard Gattinoni’s mechanical power equation (MPstd), which is considered difficult to calculate manually by healthcare professionals at the bedside. Analysis of the results, using univariable logistic regression analyses, showed that MPdyn and MPstd equation correlated significantly (R-squared=0.98). No statistically significant difference was found between MPdyn and MPstd in Bland-Altman analysis with patient power means. These results suggest that physicians may easily calculate mechanical power using MPdyn at the bedside in patients on volume control mode with different PEEP and I:E ratios. The authors concluded that although there is not enough data to show the reliability of power values computed by the MPdyn equation in ventilator modes other than volume control, it has the potential to monitor power values to identify the risk of VILI.




 Back to lobby
Back to lobby 


